For parking or stopping on the roadside define:
Vehicle routing decisions of the type Parking Lot work similarly to vehicle partial routes (Modeling vehicle routes, partial vehicle routes, and routing decisions). However, instead of routes, the desired number of parking lots is assigned. In the attributes of the vehicle routing decision type Parking lot you can specify (Attributes of parking lots):
A parking lot is created in the Network editor on a lane (Defining parking lots). If the lane does not continue downstream of the parking lot, the emergency stop position of the first downstream connector must not be tangent to the parking lot (Attributes of connectors).
The beginning of a parking lot must be positioned in movement direction and at a sufficient distance further downstream of the corresponding vehicle routing decision of the type Parking lot. This allows vehicles enough time to slow down and safely reach the first parking space. Otherwise, it might not be possible to allocate a vehicle to the first parking space(s), or the vehicle might miss its assigned parking space and block the traffic flow.
If the parking lot is located on a single-lane link, vehicles parked there might hinder free traffic flow on this link. With each time step, vehicles heading for a parking space in this parking lot check whether there is another parking space available. The vehicle thus drives far downstream in order to move up if possible and if the value of the Attraction attribute has been set so high that the parking space downstream is more attractive than the parking spaces upstream.
The parking space is assigned when the vehicle crosses a vehicle routing decision of the type Parking lot. Vissim assigns a parking space to the percentage of vehicles specified in the Parking rate attribute of the vehicle routing decision. In doing so, the vehicle classes selected, including PT vehicles, are taken into account. The vehicles Vissim has already assigned a parking space are not considered.
Vissim selects the parking lot and parking space depending on the following attributes (Attributes of parking lots):
A parking space is only assigned if the following conditions are met:
In the conditions are met, the vehicle is assigned the best suitable parking space when it traverses the vehicle routing decision of the type Parking lot. The best suitable parking space is determined based on the attribute Attraction. If multiple parking spaces have the same attraction, Vissim choses one of them based on uniform distribution. The vehicle needs at least 2 cm more space for parking than the length of the parking space.
If a parking lot only consists of a single parking space, a vehicle may park there if it is maximally as long as the parking space.
If the vehicle is longer than a parking space, Vissim checks whether two or more adjacent spaces are available to accommodate the vehicle. If a vehicle takes up all the parking spaces of a parking lot, the vehicle may park there if it is maximally as long as the total length of the parking spaces. If a vehicle does not take up all the parking spaces of a parking lot, the vehicle may park there if the total length of the parking spaces is at least 0.5 m longer than the vehicle. This ensures that there is sufficient space for pulling into and out of the parking space and the other adjacent parking spaces.
Parking spaces that are only partly used by a vehicle will not be assigned to another vehicle and are considered occupied. A vehicle always come to a standstill at the beginning of a parking space. If there are not enough adjacent parking spaces available for the long vehicle, it does not park, but continues on its route.
Vissim automatically generates vehicle routes that lead from the vehicle routing decision of the type Parking lot to each parking space of the corresponding parking lots. You cannot change these internal vehicle routes.
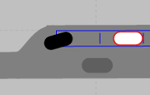
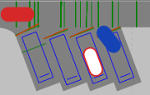
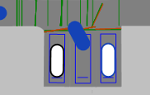
During the simulation, vehicle movements are displayed realistically for vehicles pulling into and out and in reverse of a parallel, diagonal or perpendicular parking lot. Once the vehicle has reached its final parking position in the parking space, in 2D mode, the vehicle inside is highlighted in white (by default). Examples:
| Parallel parking lot | Diagonal parking lot | Perpendicular parking lot |
|---|---|---|

|

|

|
For the Parking duration attribute of the parking routing decision, you can select the desired time distribution. The parking duration begins when the vehicle is parked in the parking space in the direction of travel and the traffic on the adjacent lane, previously blocked, can flow again.
If a parking space has not been assigned to a vehicle and no vehicle is parked in it, it is considered free. Vissim can then assign it to a vehicle. This is also the case, if the parking space can currently not be reached, as it is blocked by a vehicle, e.g. because of a traffic jam.
A parking space is considered occupied and is not assigned to another vehicle, if:
After the dwell time, the vehicle leaves the parking space via an automatically generated route that guides it back to its original route.
|
|
Note: Vissim determines the shortest path, in terms of time, to a position downstream of the parking lot routing decision. For generation of the route that takes the vehicle from the parking lot back to the route network, Vissim accounts for the entire route as well as for the current position of the vehicle on the parking lot it wants to leave. Thus, a vehicle might travel part of its original route twice or skip part of it. |
The vehicle drives forward into the parking space. The vehicle cannot back into a parking space. The Parking direction attribute of the parking space defines whether the vehicle pull outs of a parking space forward or in reverse (Attributes of parking lots). This allows the vehicle to pull into and out a parking space in the following parking directions:
A vehicle only selects a parking space that is not occupied or blocked by another parking vehicle.
In the following cases, an available parking space is blocked by another vehicle that is either parked in the space or on a lane next to an available space:
As soon as a vehicle traverses the section of a vehicle routing decision of the type Parking lot, Vissim checks its vehicle routes and the corresponding parking lots. Vissim then finds and occupies a parking space for the vehicle. With every time step, Vissim checks for all vehicles that do not have the status Waiting, whether the occupied parking space is still accessible. If the parking space is still accessible and lies on a link with a single lane, or if the parking space is no longer accessible, Vissim will look for an accessible parking space that is available. This parking space must be located on a parking lot downstream of the current parking route of the vehicle.
If the parking space chosen for a vehicle is still available when the vehicle traverses the decision point, but is occupied right before it arrives there, the vehicle will choose another parking space. Precondition: There is still a parking space available further downstream, on the route of the parking routing decision.
If an attractive parking space becomes available after the vehicle has traversed the decision section, the vehicle drives towards the originally selected parking space as long as it is still accessible.
If the vehicle cannot park on any of the parking spaces because there are not enough spaces available and accessible, the vehicle routing decision of the type Parking lot is ignored. The vehicle continues driving on its original route.
If on a lane with multiple parking spaces in a row, one or several of the spaces are occupied or reserved, the driver of a vehicle will choose a parking space further upstream that is located before the other available parking spaces. This is also true if the Attraction attribute suggests a parking space further downstream. With each time step, the driver of the vehicle checks whether in the meantime a more attractive parking space has become available and changes its destination accordingly.
If a vehicle passes a vehicle routing decision of the type Parking lot and there is no free parking space, you can set the attribute Full occupancy behavior to specify what you want the vehicle to do in this case (Attributes of parking routing decisions):
Requirements for a parking space to be reserved:
On its way to a reserved parking space, the vehicle does not look for another free parking space.
The vehicle continues driving in the following cases:
