The aim is the automatic generation of links between two sets of nodes. All nodes marked in the network are origin nodes. Destination nodes are all nodes active at the beginning of the procedure.
1. Mark the nodes that you want to connect with destination nodes.
2. If required, set the nodes active which you want to connect with origin nodes via
- the spatial selection (Setting network objects active/passive via the spatial selection) and/or
- filter criteria (Using filters to set network objects active or passive).
3. In the Network window, right-click the Nodes button.
A shortcut menu opens.
4. Select the Connect nodes via links entry.
|
Tip: Alternatively, you can right-click any node in the network and select the entry on the shortcut menu. |
The Connect nodes via links window opens.
5. Make the desired changes.
|
Section Configuration |
|
|
Element |
Description |
|
Link type |
Use the drop-down list to select the link type for the links to be inserted. All links will use the values of this link type for the following attributes:
|
|
Minimum number of new links per origin node |
Minimum number of new links that must be generated per origin node Enter a value that is greater than or equal to the number of specified destination nodes. |
|
Maximum number of new links per origin node |
Maximum number of new links that must be generated per origin node Enter a value that is less than or equal to the number of specified destination nodes, or equal to the minimum number. |
|
Radius: |
The radius defines the perimeter of each origin node that is searched for destination nodes. If there are no destination nodes within this radius or not enough to reach the minimum number, as many of the nearest nodes outside of the radius are used as destination nodes as are required to reach the necessary number (Example 1: Radius and maximum number of destination nodes and Example 2: Radius minimum and maximum number). Default value: 10 km.
|
|
Section Node count |
|
|---|---|
|
Element |
Description |
|
Number of destination nodes (active): |
Number of all active nodes in the network |
|
Number of origin nodes (marked): |
Number of all nodes marked in the network Note If no nodes are marked in the network, you can use a formula to specify which nodes in the network shall be regarded as origin nodes, as with formula attributes (Type-dependent attributes) |
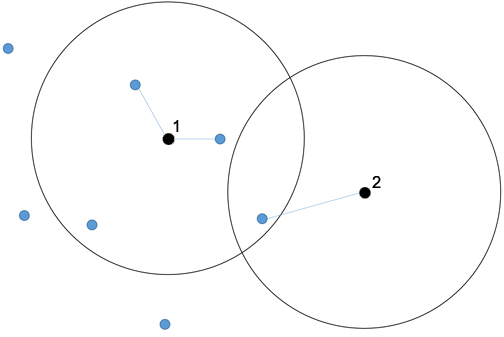
Example 1: Radius and maximum number of destination nodes
We assume an arbitrary radius, a maximum number of n, and a minimum number of 0. If more than n destination nodes are located within the circle, only the n nearest destination points within the circle will be considered. If less than n destination nodes are located within the circle, only these nodes will be considered.
The following graphics illustrates both scenarios once again (n=2). Node 1 is connected to two destination nodes, even though there are three nodes within the circle. Node 2 is connected to one destination node only.
Example 2: Radius minimum and maximum number
Again we assume a radius. Let the minimum number be 2, the maximum number 3. In the graphics below, node 1 is connected to the maximum number of nodes within the radius. Only one destination node is located within the radius of node 2; another destination node must be used from outside of the circle.
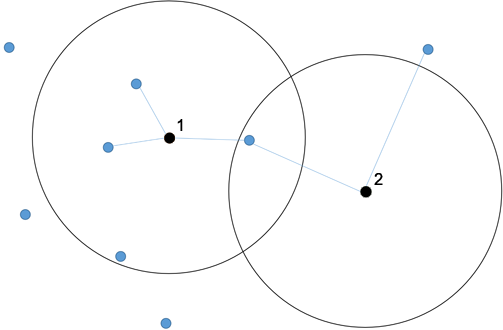
 If the option has been selected, you can specify a radius in which the destination nodes shall be located.
If the option has been selected, you can specify a radius in which the destination nodes shall be located. If this option has not been selected, all possible destination nodes are considered.
If this option has not been selected, all possible destination nodes are considered.
