Transport supply indicators express operational efforts in length units or in time units. Demand data is not required for their calculation.
|
Indicator |
Description |
|
Service kilometers |
Kilometers traversed by vehicle journeys. Trip length via all vehicle journeys and number of departures. |
|
Section service kilometers |
Compared to ServiceKm, the length of each individual vehicle journey section is added (as long as it lies within the analysis period). |
|
Service time |
Time required by vehicle journeys. Trip length via all vehicle journeys and number of departures. |
|
Section service time |
Compared to service time, the duration of each individual vehicle journey section is added (as long as it lies within the analysis period). Also the dwell time between adjacent vehicle journey sections is included. |
|
Empty kilometers |
Kilometers traversed by empty trips. Compared to vehicle journeys, no passengers are carried on empty trips. Empty kilometers = Pull-out kilometers + Interlining kilometers + Pull-in kilometers |
|
Section empty kilometers |
Compared to EmptyKm, the length of each individual vehicle journey section is added (as long as it lies within the analysis period). |
|
Empty time |
Time required by empty trips. Compared to vehicle journeys, no passengers are carried on empty trips. EmptyTime = Pull-out time + Interlining time + Pull-in time |
|
Section Empty Time |
Compared to empty time, the duration of each vehicle journey section is added (as long as it lies within the analysis period). |
|
Operating kilometers |
Operating kilometers = Service kilometers + Empty kilometers |
|
Section operating kilometers |
Compared to EmptyKm, the length of each individual vehicle journey section is added (as long as it lies within the analysis period). |
|
Out-of-depot time |
Operating time = Service time + Empty time |
|
Section operating time |
Compared to operating time, the duration of each vehicle journey section is added (as long as it lies within the analysis period). |
|
Stop time |
Stop time of all stop events |
|
Section stop time |
In contrast to a stop time, the stop times of overlapping vehicle journey sections are counted multiple times. |
|
Seat capacity |
Sums up the number of seats of the vehicle combinations over all vehicle journey sections of the object, for which the indicator is determined (e.g. lines). This attribute is only available for the elements of the line hierarchy and for PuT operators and transport systems. |
|
Seat kilometers |
Seat Km = Section Service Km • Number of seats of vehicle combinations Summed up over all vehicle journey sections and number of departures. |
|
Seat hours |
Seat Hours = Section Service Time • Number of seats of vehicle combinations Summed up over all vehicle journey sections. |
|
Total capacity |
Sums up the total seating and standing capacity of the vehicle combinations over all vehicle journey sections of the object, for which the indicator is determined (for example, lines). This attribute is only available for the elements of the line hierarchy and for PuT operators and transport systems. |
|
Total capacity kilometers |
Total Capacity Km = Section Service Km • Total seating and standing capacity of the vehicle combinations Summed up over all vehicle journey sections. |
|
Total capacity hours |
Total Capacity Hours = Section Service Time • Total seating and standing capacity of the vehicle combinations Summed up over all vehicle journey sections. |
|
Length |
Length covered by the time profile items in the territory (attribute is only available via Territory - PuT Detail, for level Territory x Time profile (x Vehicle combination) and Territory X Vehicle journey (x Vehicle combination)). |
|
Run time |
Travel time used to cover the time profile items in the territory, (attribute is only available via Territory - PuT Detail, for level Territory x Time profile (x Vehicle combination)). |
|
Mean Speed |
Mean speed = Service kilometers / Service time |
|
Capacity PuT Seats |
Number of seats of vehicle combinations, which traverse this link, summed up over all vehicle journey sections (Attribute is only available for links). |
|
Capacity PuT total |
Total seating and standing capacity of the vehicle combinations, which traverse this link, summed up over all vehicle journey sections and the number of departures (Attribute is only available for links). |
|
Number of Vehicles (in proportion to length) |
The number of vehicles which are - according to the current block version - required for the reference object, (line, line route, etc.). The indicator value corresponds to the number of blocks, which cover the vehicle journey sections of the reference object. If a block covers vehicle journey sections of several objects, for the vehicle the proportion of the vehicle journey sections and optionally of the unproductive distances (such as empty trips) of the reference object is added to the line length of all vehicle journey sections. |
|
Number of vehicles (in proportion to time) |
As above, but the addition to the reference object is instead carried out with the share of vehicle journey sections and optionally with the share of unproductive periods (such as layover and setup times) of the reference object in the service time of all vehicle journey sections. |
Table 245: Indicators of the transport supply
Calculation example: Service kilometers per transport system
- Service km for the analysis period = Number of trips (AP) • Trip length.
For the bus it applies that ServiceKm (AP) = 38 • 27.5 km + 38 • 7.5km = 1,045 km + 285 km = 1,330 km
For the train it applies that ServiceKm (AP) = 38 • 10 km = 380 km
- Service km for the analysis horizon = Service km (AP) • Projection factor of the valid day
For the bus it applies that ServiceKm (AH) = 1045 km • 365 + 285 km • 260 = 455525 km
For the train it applies that ServiceKm (AH) = 380 km • 365 = 138700 km
- Service km for the analysis time interval TI1 results from summing up the km data from all trip sections, whose respective line route items depart in this time slice
For the bus it applies that ServiceKm (TI1) = 113.75 km. The calculation is made clearer by Illustration 204.
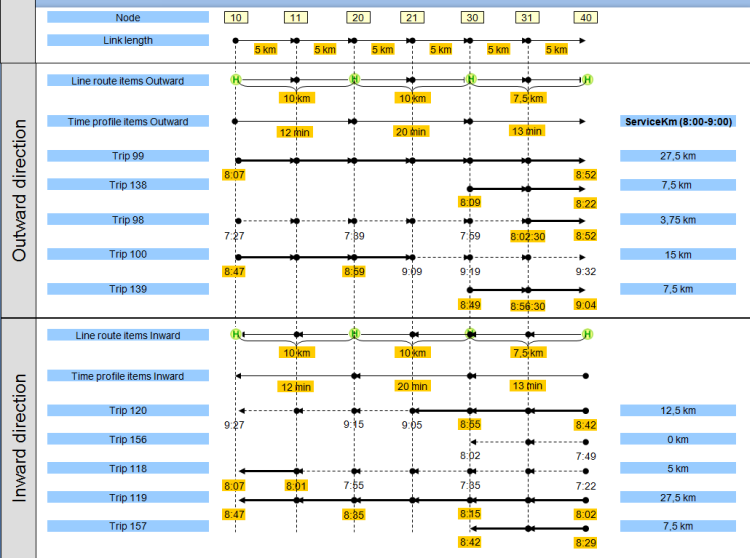
Illustration 204: Calculation of service kilometers between 8 a.m. and 9 a.m.
For the train it applies that ServiceKm (TI1) = 3 • 10 km = 30 km (Trip numbers 61, 80, 81)
Calculation example: Seat km per transport system
- Seat km for the analysis period = ServiceKm (AP) • Number of seats summed up over all trip sections.
For the bus it applies that SeatKm (AP) = 1330 km • 35 = 46550 km
For the train it applies that SeatKm (AP) = 380 km • 200 = 76000 km
- Seat km for the analysis horizon = Seat km (AP) • Projection factor of the valid day summed up over all trip sections.
For the bus it applies that SeatKm (AH) = 38 • 262.5 km • 260 + 38 • 962.5 km • 365 = 15,943.375 km
For the train it applies that SeatKm (AH) = 76000 km • 365 = 27740000 km
- For seat km in the analysis time interval TI, the calculation is analog to the service km calculation (Illustration 204).
For the bus it applies that SeatKm (TI) = 35 • (27.5 + 3.75 + 15 + 12.5 + 5 + 27.5) km + 35 • (7.5 + 7.5 + 7.5) = 3,981.25 km
For the train it applies that SeatKm (TI) = 30 km • 200 = 6000 km
Calculation example: Service time per transport system
- Service time for the analysis period = Num PuT Departures (AP) • Times from Time profiles
For the bus it applies that ServiceTime (AP) = 38 • 45 min + 38 • 13 min = 2204 min = 36 h 44 min
For the train it applies that ServiceTime (AP) = 38 • 16 min = 608 min = 10h 8 min
- Service time for the analysis horizon = Service time (AP) • Projection factor of the valid day summed up over all trip sections.
For the bus it applies that Service time (AH) = 38 • 45 min • 365 + 38 • 13 min • 260 = 752590 min = 12543 h 10 min
For the train it applies that Service time (AH) = 38 • 16 min • 365 = 221920 min = 3698h 40 min
- Service time for the analysis time interval TI: Calculation is done analog to the service kilometer calculation (Illustration 204).
For the bus it applies that service time (TI) = 45 min + 13 min + (5 km/10 km) • 13 min + 12 min + (5 km/10 km) • 20 min + 13 min + 13 min + (5 km/10 km) • 20 min + 0 min + (5 km/10 km) • 12 min + 45 min + 13 min = 186.5 min = 3 h 10 min
For the train it applies that Service time (TI) = 3 • 16 min = 48 min
Calculation example: Mean speed per PuT line
- Mean speed = ServiceKm(AP) / ServiceTime (AP)
For the bus it applies that vMean = 1330 km / 36h 44 min = 36.2 km/h
For the train it applies that vMean = 380 km / 10 h 8 min = 37.5 km/h

