A timetable-based PuT assignment produces connections (PuT paths) and their volumes. Based on these connections, the total risk of delay or the risk of delay of the individual persons using the connections can be determined. The search procedure Branch and Bound search is used when searching for connection alternatives. For this, impedance and choice parameters are required (Connection search using Branch and Bound).
These parameters are also used if connections are loaded from another file or adopted from another demand segment.
To analyze the risk of delay, you need the probability POnTime as an input parameter for each vehicle journey item, indicating how likely it is to be on time. Therefore, only vehicle journey items with POnTime∈(0,1) are considered in the analysis, as only these can be delayed. In addition, you must specify parameter λ > 0 as exponent for exponential distribution. The exponential distribution weights the possible travel time extensions by using a later connection. In addition, a termination value specifies from which function value of the exponential distribution the associated delay is no longer considered.
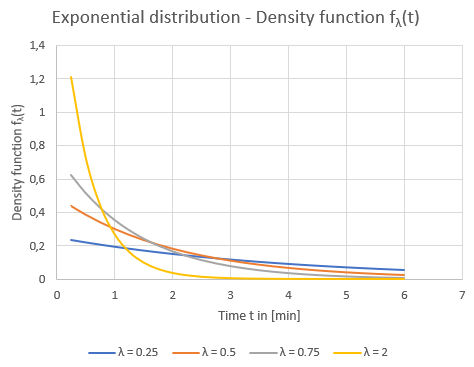
Illustration 164: Exponential distribution diagram - density function fλ(t)
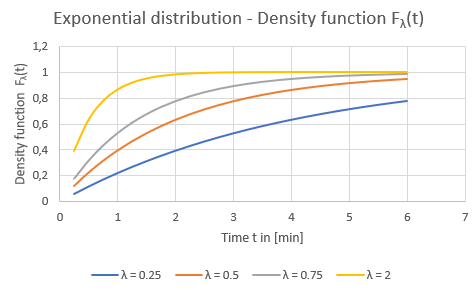
Illustration 165: Exponential distribution diagram - distribution function Fλ(t)
In addition, you must define from which duration trelevant a delay is relevant. This value is required for the calculation of the share of persons considered relevant.
Furthermore, there are:
- the maximum analyzed delay tmax, which specifies the maximum delay up to which the analysis is performed.
- the assumed travel time extension t̅ if no alternative connection could be found.
In addition, the calculation can take into account the probability that a connection
between two vehicle journey items f and g can be reached despite delay. For this purpose, a planned connection can be specified for each connection. The planned connection is either specified via a guaranteed wait time from the connection trip to the arriving vehicle journey or via a connection probability
.

