The effectiveness of the equilibrium assignment is described in the example in Table 135 and Illustration 95. The example analyzes the relation between traffic zone "village A" and traffic zone "city X".
For simplicity, the total impedance of a route is the sum of the link impedances of the route (Impact models), i.e. the impedances of the connectors and turns are not modeled in this example. In detail, the following assumptions apply:
- The impedance of the links is determined from the current travel time tCur. The current travel time tCur is in turn calculated using the capacity restraint function BPR with a=1, b=2 and c=1.
- The access and egress times for the connectors are not considered, that is, they are set to 0 minutes.
- Turn penalties are not considered.
With regard to the traffic demand the following applies.
- The traffic demand between A-Village and X-City is 2,000 car trips during peak hour.
- Capacity and demand refer to one hour.
The example network contains three routes which connect village A and city X.
- Route 1 via nodes 10 – 11 – 41 – 40
- Route 2 via nodes 10 – 11 – 20 – 21 – 30 – 31 – 40
- Route 3 via nodes 10 – 12 – 21 – 30 – 31 – 40
Route 1 mainly uses country roads and is 26 km long. It is the shortest route. Route 2 is 30 km long. It is the fastest route because the federal road can be traversed at a speed of 100 km/h if there is free traffic flow.
Route 3 which is also 30 km long is an alternative route which only makes sense if the federal road is congested.
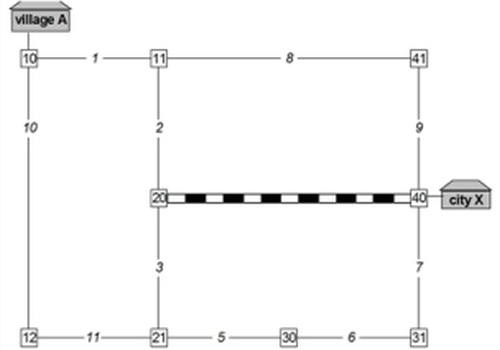
Illustration 95: Example network for equilibrium assignment
|
LinkNo |
From Node |
To Node |
Type |
Length [m] |
Capacity [car units/h] |
v0-PrT [km/h] |
|
1 |
10 |
11 |
20 Federal road |
5000 |
1200 |
100 |
|
2 |
11 |
20 |
20 Federal road |
5000 |
1200 |
100 |
|
3 |
20 |
21 |
20 Federal road |
5000 |
1200 |
100 |
|
4 |
20 |
40 |
90 Rail track |
10000 |
0 |
0 |
|
5 |
21 |
30 |
20 Federal road |
5000 |
1200 |
100 |
|
6 |
30 |
31 |
20 Federal road |
5000 |
1200 |
100 |
|
7 |
31 |
40 |
20 Federal road |
5000 |
1200 |
100 |
|
8 |
11 |
41 |
30 Country road |
16000 |
800 |
80 |
|
9 |
40 |
41 |
30 Country road |
5000 |
800 |
80 |
|
10 |
10 |
12 |
40 Other roads |
10000 |
500 |
60 |
|
11 |
12 |
21 |
40 Other roads |
5000 |
500 |
60 |
As a result, the assignment provides values of Table 136 for the three routes (PrT paths).
|
Route |
tCur |
t0 |
Impedance |
Volume (AP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
18min 45s | 38min 20s | 2300 | 736.431 |
|
2 |
18 min | 38min 20s | 2302 | 994.102 |
|
3 |
24 min | 38min 20s | 2301 | 269.466 |
The most important assignment results for links are displayed in Table 137.
|
Link |
tCur |
Impedance |
Volume (AP) |
Saturation PrT (AP) |
VehicleHr(tCur) |
VehKmTravelled PrT |
|
1 |
9min 14s | 554 | 1730.533 | 144.2 % | 266h 28min 30s | 8652.669 |
|
2 |
5min 4s |
304 |
994,102 |
82.8 % |
83h 49min |
4970.510 |
|
3 |
5min 4s |
304 |
994.1024 |
82.8 % |
83h 49min |
6317.841 |
|
5 |
6min 20s | 380 | 1263.568 | 105.3 % | 133h 13min 40s | 6317.841 |
|
6 |
6min 20s | 380 | 1263.568 | 105.3 % | 133h 13min 40s | 6317.841 |
|
7 |
6min 20s | 380 | 1263.568 | 105.3 % | 133h 13min 40s | 6317.841 |
|
8 |
22min 10s | 1330 | 736.431 | 92.1 % | 272h 5min 45s | 11782.907 |
|
9 |
6min 56s | 416 | 736.431 | 92.1 % | 85h 1min 48s | 3682.158 |
|
10 |
12min 54s | 774 | 269.466 | 53.9 % | 57h 57min 19s | 2694.661 |
|
11 |
6min 27s | 387 | 269.466 | 53.9 % | 28h 58min 40s | 1347.331 |

