During ICA assignment, turn and link VD functions are modified. This is done in two ways:
- horizontal shift of the curve due to lower volumes (downstream metering)
- adjusting the curve progression for volumes exceeding effective capacity, triggered by additional traffic jam waiting times
The first adjustment is made for both turn and link VD functions via the attribute Suppressed upstream volume. The second adjustment is only made for links on which a traffic jam is observed. Both effects are depicted in the following figure of a modified link VD function.
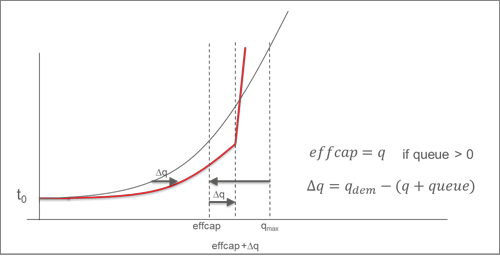
Illustration 102: Adjusting links of the VD function
Generally, link VD functions are conventionally assigned during the assignment with ICA, so you can define link VD functions based on the link type. The following equation shows the adjustments, where vdfbase refers to the link VD function you defined.
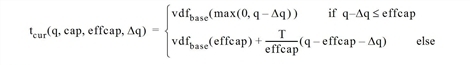
where
|
tcur |
Link run time in loaded network |
|
vdfbase |
VD function defined (depends on link type) |
|
q |
Link volume in subordinate assignment (without spillback congestion) |
|
cap |
Link capacity |
|
effcap |
Link attribute calculated in each iteration after spillback calculation The attribute Effective capacity for assignment with ICA contains the value calculated at the end of the assignment with ICA. The effective capacity corresponds to the link capacity on uncongested links. On congested links, effective capacity is given by the minimum of capacity and link volume. |
|
Dq |
Link attribute that represents the difference between demand volume and volume plus queue length. Suppressed volume refers to the part of the volume that, according to blocking back calculation, is held back upstream and so does not reach the link. Attribute Suppressed volume upstream in assignment with ICA contains the value calculated at the end of the assignment with ICA. |
|
T |
T = 1,800, i.e. T corresponds to half the assignment period [in sec] |
By adjusting the VD functions, you ensure that the impedances changed through blocking back calculation have an impact on route search and route choice in the subordinate assignment.

