Simulation-based dynamic assignment (SBA) is an iterative procedure that consists of the following steps:
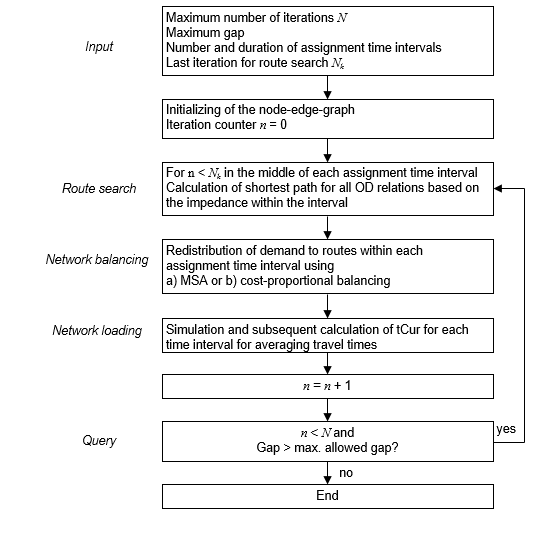
Illustration 139: Steps of simulation-based dynamic assignment
Following the simulation, after which impedances are updated based on recalculated travel times, a convergence check is performed. The relative gap serves as a convergence criterion. In addition, the results per time interval for balancing are taken into account. The gap is calculated as follows:
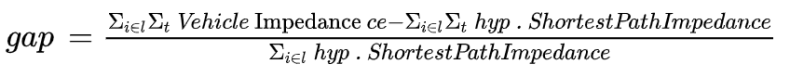
This means that vehicle impedance as well as the hypothetical shortest path vehicle impedance are summed up for all OD pairs i and all time intervals t for balancing. Similar to static assignments, the enumerator becomes smaller, the closer the actual impedance of a path is to the shortest path in the time interval. A state of equilibrium is reached, when the gap falls below a defined threshold value. In the assignment statistics, the gap and other indicators of assignment are listed per iteration, transport system and time interval.

