Dynamic stochastic assignment: Basis tab
|
Element |
Description |
|
From |
Start of the assignment time period Note If a calendar is used, you need to select a weekday or a date (Specifying a calendar and valid days). |
|
To |
End of the assignment time period Note If a calendar is used, you need to select a weekday or a date (Specifying a calendar and valid days). |
|
Interval length |
Length of time sub-intervals of the assignment period in [minutes] (Fundamentals: Dynamic stochastic assignment) |
|
Global termination condition |
Maximum number of iterations The procedure terminates after the specified number of external iterations. |
|
Termination condition for network balancing |
The termination conditions comply with those of stochastic assignment, but refer to connections instead of routes (Stochastic assignment: Basis tab) |
Dynamic stochastic assignment: Impedance tab
For each demand segment chosen for the procedure, there is an Impedance tab. By clicking on the general impedance symbol, if necessary, you can set an additional special impedance for each demand segment via the complete path. You can, for example, model bicycle or heavy goods transport better. The general impedance for each transport system is used, which is displayed in the first row, and DeltaT, an impedance component, which calculates the deviation from the desired departure time.
|
Element |
Description |
|
Coefficient |
Factor by which the impedance is multiplied. |
|
Property |
You can insert a description here. |
|
Formula |
Specify here the formula for the user-defined impedance for each path for the relevant demand segment. For bicycle traffic, for example, you can enter here the maximum slope [MAX:LINKS\SLOPE] on the entire path. |
|
Upper limit for DeltaT (early)/(late) |
Enter here the values for DeltaT (early) and DeltaT (late). The values indicate the difference cut short from the actual start time and the desired departure time. Each of these values has a β_early and β_late coefficient. |
Dynamic stochastic assignment: Smoothing tab
|
Element |
Description |
|
Route volumes |
Route volumes are calculated according to the method of successive averages (MSA). Therefore, you need to define the exponent (value range 0 – 4). Notes For smoothing the route volumes, we recommend an exponent between 1 and 1.5. With exponent = 1 the formula complies with the formula used by the method of successive averages (MSA). This ensures a safe but slow convergence. A greater value normally reduces the number of iteration steps, but does not necessarily lead to convergence. |
|
Smoothed impedances |
In the selection list, select the method for smoothing the estimated impedance. The methods provide different input options for the Delta value computation. Notes We recommend to test the three smoothing methods prior to the actual calculation. Heuristic rule Lotka-Volterra rule Note In most cases, the Lotka Volterra method is faster than the heuristic method; however, the quality of the calculation results depends on the used network. Method of successive average With this selection you define the exponent (value range 0 – 1). Notes For the exponent, we recommend a value close to 0.15. With parameter value = 1 the formula complies with the formula used by the method of successive averages. This ensures a safe but slow convergence. Do not smooth impedances This selection is used to obtain convergence faster if exponential smoothing of impedance values impairs the convergence of a procedure instead of improving it. If this entry has been selected, the currently estimated impedance equals the current impedance. |
Dynamic stochastic assignment: Search tab
In this tab, you define how to determine PrT routes.
|
Element |
Description |
|
Randomized search |
These parameters correspond to the parameters of stochastic assignment (Stochastic assignment: Search tab) |
|
Detour test |
These parameters correspond to the parameters of stochastic assignment (Stochastic assignment: Search tab) |
|
Times for the path search |
Click this button to define the times you want to use for route search (Fundamentals: Dynamic stochastic assignment). Note If no point in time is specified within the current assignment time period, Visum will use the current start time from (Dynamic stochastic assignment: Basis tab) |
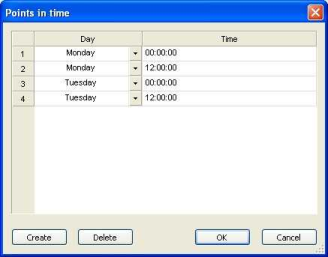
|
Element |
Description |
|
Day |
Weekday or date Note The entries depend on the calendar selected (Specifying a calendar and valid days). |
|
Time |
Times for the path search |
|
Create |
Via this button, you add a new row. |
|
Delete |
Via this button, you remove the currently selected row. |
|
Note: After closing the window and calling it again, the entries will automatically be sorted in chronological order. |
Dynamic stochastic assignment: Preselection tab
In this tab, you define how to select the routes found (Stochastic assignment: Preselection tab).
Dynamic stochastic assignment: Choice tab
In this tab, you specify how to distribute the demand to the connections found (Stochastic assignment: Choice tab).

