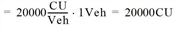The costs for a vehicle is composed of hourly costs, kilometer costs and fixed costs. In Visum, these costs are assigned to vehicle units (User Manual: Vehicle-bound costs). In practice these kilometer and vehicle costs are dependent on the vehicle type used (for example standard or articulated bus, or tram in single or multiple traction) and the hourly costs of the operator (for example public or private operator, type of labor contract).
Hourly costs (attribute Cost time)
Time costs = service time • hourly costs rate of vehicle journeys + empty time • hourly cost rate of empty trips
- Service time describes the time for passenger transport. It can be taken from the timetable.
- Empty time comprises the times for delay buffers, driver breaks or interlining and layover. Line blocking is required for determining the empty times, otherwise this share is not included in the hourly costs.
Kilometer costs (attribute Cost distance)
Distance costs = ServiceKm • kilometer cost rate of vehicle journeys + empty kilometers • kilometer cost rate of empty trips
- Service kilometers for transporting passengers are calculated directly from the vehicle journeys in the timetable.
- Empty kilometers arise from empty trips between the last stop of a service trip and the first stop of another service trip, within a block.
Vehicle costs (attribute Cost vehicle)
Vehicle costs result from the fixed costs, which can be defined for each vehicle unit (User Manual: Properties and options of vehicle units), and the vehicle demand determined by PuT line blocking.
Vehicle costs = cost rate per vehicle unit • number of vehicles
- The attribute Cost rate per vehicle unit contains the fixed costs for each vehicle unit (the acquisition costs for example). Fixed costs increase with every additional vehicle required.
- The value Number of vehicles results from the necessary vehicle blocks. Line blocking is therefore assumed for the calculation of vehicle costs.
Calculation example: Vehicle type-dependent costs for lines
This example regards the following vehicle type-specific cost rates (Example for PuT operating indicators).
|
Vehicle units |
Standard bus |
Low floor bus |
Train |
|||
|
|
Service |
Empty |
Service |
Empty |
Service |
Empty |
|
Cost rate per hour [CU/h] |
300.00 |
200.00 |
300.00 |
200.00 |
700.00 |
500.00 |
|
Cost rate per km [CU/km] |
5.00 |
5.00 |
5.00 |
5.00 |
10.00 |
10.00 |
|
Cost rate per vehicle unit [CU/Veh] |
7000.00 |
7000.00 |
20000.00 |
|||
|
Reference period of the cost rate per vehicle unit |
Analysis period |
Analysis period |
Analysis period |
|||
Table 250: Cost rates for the vehicle units
|
Vehicle combinations |
Standard bus |
Low floor bus |
Train |
|||
|
|
Service |
Empty |
Service |
Empty |
Service |
Empty |
|
Cost rate per hour [CU/h] |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
50.00 |
50.00 |
|
Cost rate per km [CU/km] |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
The following distances and times accumulate for the train:
|
Vehicle combination |
ServiceKm |
EmptyKm |
Service time |
Empty time |
|
Train |
380 km |
0 km |
10.13 h |
0 h |
Calculating the vehicle type-dependent costs (distance costs, time costs and vehicle costs) for lines returns the following result for the Train line.
- Distance costs / analysis period
CostDist(AP) = CostKmService • ServiceKm(AP) + CostKmEmpty • EmptyKm(AP)
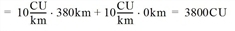
- Time costs / analysis period
CostTime(AP) = CostTimeService • ServiceTime(AP) + CostTimeEmpty • EmptyTime(AP)
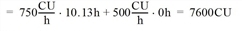
- Vehicle costs / analysis period
CostVehicle(AP) = Cost rate vehicle unit • Number of vehicles