To assess the convergence speed, Visum logs convergence criteria for all static assignment procedures (except incremental assignment) for each iteration. Stochastic assignment only logs the internal iterations within the last external iteration (Stochastic assignment).
These criteria are output in a list as indicators of the quality of a PrT assignment (User Manual: Viewing convergence criteria and convergence speed). They are reset prior to each assignment and stored with the version file.
Among others, the following criteria are calculated:
- Hypothetic vehicle impedance
Minimum impedance value calculated hypothetically for the next iteration step on the assumption that all vehicles – based on the current impedances in the network – use the best path.
- Gap = (veh. imp. - hypothet. veh. imp.) / hypothet. veh. imp.
Degree of convergence for the network.
The value is the weighted volume difference between the vehicle impedance of the network of the current iteration and the hypothetical vehicle impedance.
- Total excess cost TEC
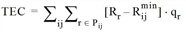
where
|
TEC |
Difference between the total impedance in the loaded network and the hypothetical impedance resulting if all vehicles took the shortest path for their OD pair. |
|
Pij |
Number of routes from i to j |
|
Rijmin |
minimum impedance among all routes from i to j |
- Average excess cost AEC
AEC = Excess cost per vehicle
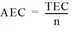
The following applies:
n = Number of trips: Total demand in the demand matrix minus the diagonal, thus the sum of demand contributing to the assignment, no internal traffic.
For the analysis of the convergence behavior, there are extended stability criteria for the static assignment procedures Equilibrium, LUCE, and Bi-conjugate Frank Wolfe (BFW). These criteria were defined on the basis of existing guidelines, such as the criteria of the "TAG unit M3-1 Highway Assignment Modelling" (DfT 2014) guideline, and can optionally serve as termination conditions for assignment. The shares for each network object type are displayed in the assignment quality list regardless of whether the criteria are valid as termination conditions. More specifically, this means that thresholds for the relative deviations between volumes and impedances are defined in successive iterations and the shares of network objects that must meet these thresholds is determined. Alternatively, the relative deviations for individual network objects can be output in user-defined attributes so that changes in volumes or impedances can be analyzed via the iterations and displayed graphically in the network. In addition, the number of successive iterations in which a network object has fulfilled the thresholds is stored.
A restriction to active network objects is optionally possible, so that the evaluation of the extended stability criteria for parts of the network of low interest can be excluded from the outset.

