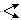Relation types of indirect attributes
In the classical sorting, indirect attributes are listed at the bottom of the list. They can be related to the network object in three different ways. These relations are called relation types in Visum. The following indicators depict the relations between the currently selected network object type and its indirect attributes:
|
Indicator |
Description |
|
|
The network object has got exactly one associated network object in the respective category. |
|
|
The network object has got either exactly one or no associated network object in the respective category. |
|
|
The network object has got several associated network objects in the respective category. These are aggregated by aggregation functions. |
|
|
Aggregation function |
|
Note: If you position the mouse pointer on an indirect attribute, a tooltip indicates the full path, the name, an explanation and the origin of the attribute. |
Aggregation functions of indirect attributes
If you expand a relation of a network object with several associated network objects, aggregation functions are displayed. These indicate how the associated network objects are aggregated. They refer to either all objects (Count) or all active objects (CountActive) of the relation.
- Count and CountActive (Number of all associated network objects)
- Min and MinActive
- Max and MaxActive
- Sum and SumActive
- Avg and AvgActive
- Concatenate and ConcatenateActive
- Histogram and HistogramActive
- Distinct and DistinctActive
- Compare and CompareActive
- First and FirstActive
- Last and LastActive
- ExactOne (returns the value of an object if there is exactly one object)
For relations that refer to several objects, you can also specify a condition in the aggregation function (Fundamentals: Relations with conditions). In this case, only the objects that fulfill this condition are output and aggregation takes place using these objects.
Example
[SUM:TURNS([TYPENO]=2)\VOLVEHPRT(AP)] as a formula for the sum of all straight turns at a node.
|
Notes: You can use the aggregation function Histogram to get a quick overview of an attribute of another network object, for example, the link types of all links of a node. Identical values will then be displayed in groups. These aggregation functions only refer to the output of attribute values in lists, graphic parameters, filters or in the Quick view. |