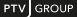This section describes how to convert the formulation used in WebTAG (Department for Transport 2017) for use in a Visum model. To simplify the description, we will be looking at an absolute model form, a model structure without time-of-day choice and only two levels: the mode choice with the alternatives car and PT on the upper level and the destination choice on the lower level.

The following indices are used:
- Origin zone of the trip: i
- Destination zone of the trip: j with the alternatives k
- Modes m with the alternatives r
The following quantities are also used:
- Generalized cost (negative utility at the leaf nodes of the decision tree): G
- Composite utility (utility at the nodes above the leaf nodes of the decision tree): U
- Trips: T
- Attraction factors: Aj in Visum and Bj in WebTAG
Finally, there are the following scaling parameters:
- Distribution parameter:
- Mode choice parameter:
in Visum and
in WebTag
In Visum, scaling parameters are used for all nodes except the leaf nodes, i.e. at the root node there are for mode choice and at the destination choice nodes
and
.
The following section describes the Visum formulation:

For utility Uim (mϵ{car,PT}) this results in:

For the demand Tim (mϵ{car,PT}) this results in:
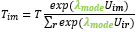
And at the lowest level:
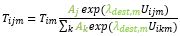
The following shows the same model structure with the formulation used in WebTAG.
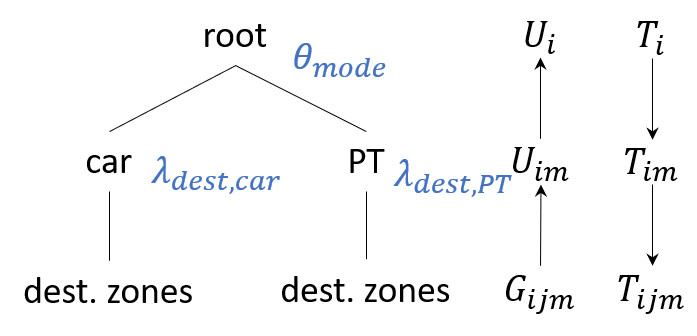
In WebTAG,  and
and  are also on the level of destination choice. At the level of mode choice, however, there is
are also on the level of destination choice. At the level of mode choice, however, there is  . In general, this results in
. In general, this results in 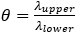 , i.e. the quotient of λ of the same level and λ of the level below. The problem is that in the WebTAG formulation there are two different λ on the lower level, which should lead to two different θ.
, i.e. the quotient of λ of the same level and λ of the level below. The problem is that in the WebTAG formulation there are two different λ on the lower level, which should lead to two different θ.
According to the WebTAG formulation, the utility is calculated based on Uim (mϵ{car,PT}):
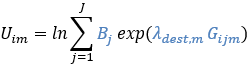 .
.
According to WebTAG, for demand Tim (mϵ{car,PT}) this results in:
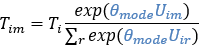
And at the bottom level:
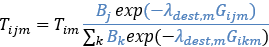
There are two ways to model the WebTAG formulation in Visum. In both cases, Aj = Bj can be set. In addition, the same λ are needed on the bottom level.
One option is to set 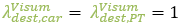 .
.
If at the level of the leaf nodes the utility is defined by

then the result is:
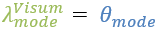
As a result, the Visum formulas are converted into WebTAG formulas.
An alternative would be to set λ on the top level to 1, i.e.:

In addition, you set:
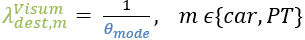
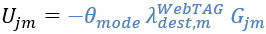
As a result, the Visum formulas are converted into WebTAG formulas.
The same way, model structures with time of day choice can be converted from WebTAG into the Visum formulation. We assume the following model structure to this end:

In the WebTAG formulation, there is λ on the level of destination choice, namely:
λdest,car,AM, λdest,car,PM, λdest,PT,PM, λdest,PT,PM, θ on the level of time-of-day choice, θtime,car and/or θtime,PT and θmode on the top level of mode choice.
For conversion to Visum, Aj = Bj must be set here as well. As described for the previous structure, there are several ways to convert the WebTAG formulation into Visum formulas. The most direct and simplest form is as follows:

It can also be shown for this model structure that the WebTAG formulas can be converted into the Visum formulation.
The model structures listed here are examples. In principle, this is how all WebTAG model formulations can be converted into Visum.