A typical use case for an intersection is the data import from a GIS.
- Land use data is available in GIS.
- Land use data is imported into Visum using a shape file, which is read in a POI. Alternatively Visum can be connected to a Personal Geodatabase. Land use data in Visum are then available as GIS objects.
- The zone and an editable attribute are later selected as target object, to adapt the created information.
- Through the intersection of zones and POIs the result is the land use data per zone and can for example be used in a Visum demand model (for example the number of homes per zone).
Intersection is not just confined to data exchange with GIS. Multiple application possibilities also arise within Visum. Some examples, which information can be obtained with an intersection operation are introduced in the following.
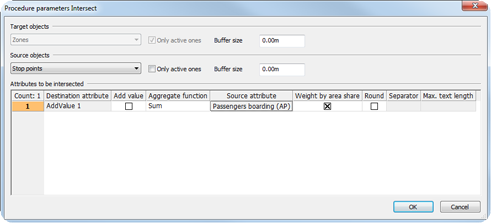
- Number of boarding PuT passengers per zone (Table 274)
- Number of inhabitants in the catchment areas of line routes (Table 275)
- Vehicle kilometers within territories (Table 276)
- Numbers of the stops within a zone (Table 277)
|
|
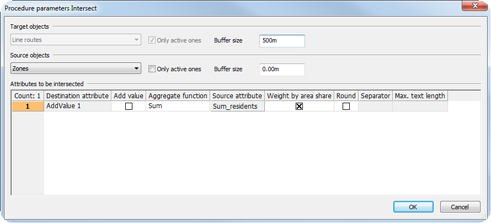
Intersecting line routes and zones: The inhabitants of a line route are calculated from LineRoute.AddValue1 = Sum of inhabitants in zones within a 500m buffer around the line route |
|
|
|
Table 275: Calculating the number of inhabitants in the catchment areas of lines
|
|
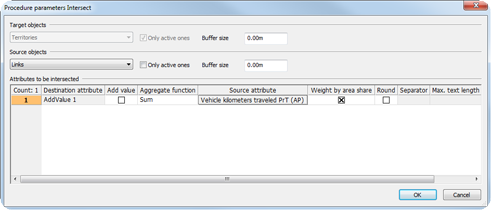
Intersecting territories and links: The vehicle kilometers in a territory are calculated from Territory.AddValue1 = Sum of VehicleKm PrT via all links in a territory. |
|
|
|
Table 276: Calculating the vehicle kilometers within territories
|
|
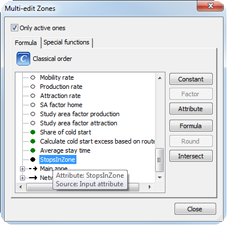
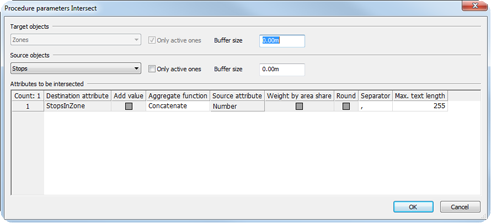
Intersecting zones and stops: which stops lie within a zone. As target attribute, a user-defined attribute of the type Text is used, to which a concatenated list of the numbers of the stops will be saved. |
|
|
|
Table 277: Determination of the numbers of the stops that lie within a zone
|
Note: If you want to calculate the number of source objects per target object, select the attribute 1.0 of the source object. |