The steps of the 4-step model performed according to prescribed sequential calculation are carried out in the following sequence: trip generation, trip distribution, mode choice and assignment. As Image 50 indicates, utility matrices are used for the model steps trip distribution and mode choice. They are mainly calculated based on skim matrices from the assignment.
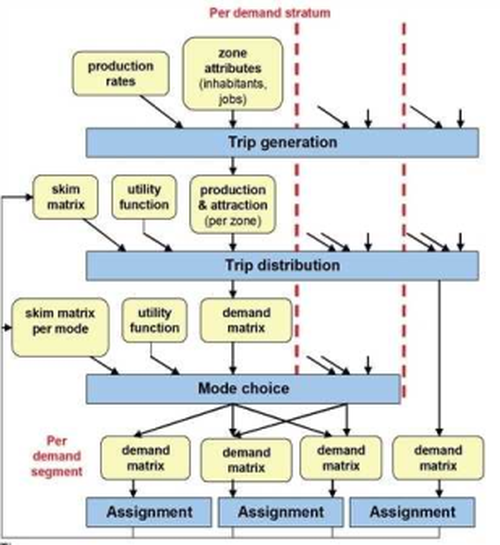
Image 50: Integrated 4-step model with sequential calculation in Visum
You can also improve convergence speed by averaging the demand matrices or impedances of successive iterations within the loop. To do so, you can e.g. use the function Average determination according to MSA (Average determination using the Method of Successive Averages (MSA)).
As an extension of the conventional 4-step model, you can calculate mode choice in multiple steps instead of in a single step (nested logit within the procedure nested demand). You can optionally add a departure time after mode choice. The Image 51 illustrates the procedure in such an extended demand model.
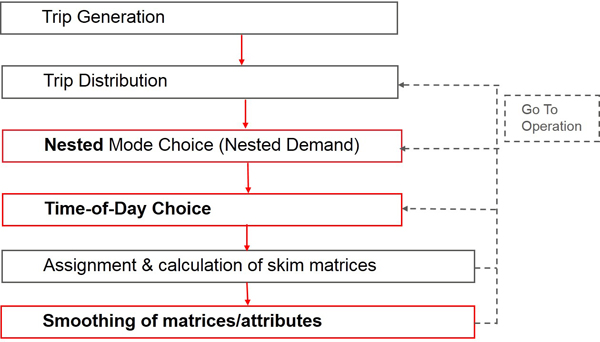
Image 51: Extended 4-step model with sequential calculation
You normally carry out the procedures trip generation, trip distribution and mode choice for all demand strata of the model. However, for special purposes you may perform them for individual demand strata, as long as the required input attributes or matrices are known.
If necessary, additional operations on matrices may be fitted in between the individual stages, for example in order to prepare skim matrices (e.g. setting the values on the matrix diagonal) or to add externally predetermined demand data (e.g. through-traffic) (Displaying and editing matrices).