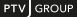|
|
Route |
Volume |
tCur [min] |
|
Starting solution |
1 |
1,000 |
51:42 |
|
Routes 1 + 2 are known |
2 |
1,000 |
36:45 |
|
|
3 |
0 |
30:15 |
|
Network balancing 0 |
1 |
776 |
41:54 |
|
Routes 1 + 2 |
2 |
1,224 |
41:56 |
|
|
3 |
0 |
33:22 |
|
Iteration step 1: route search finds route 3 |
|||
|
Network balancing 1 |
1 |
649 |
36:25 |
|
Routes 1 + 3 |
2 |
1,224 |
42:58 |
|
|
3 |
127 |
36:23 |
|
|
Max. imp. route = 2, Min. imp. route = 3 |
||
|
Network balancing 2 |
1 |
649 |
35:15 |
|
Routes 2 + 3 |
2 |
1,067 |
40:17 |
|
|
3 |
284 |
40:15 |
|
|
Max. imp. route = 2, Min. imp. route = 3 |
||
|
Network balancing 3 |
1 |
734 |
38:09 |
|
Routes 1 + 2 |
2 |
982 |
38:10 |
|
|
3 |
277 |
38:51 |
|
|
Max. imp. route = 3, Min. imp. route = 1 |
||
|
Network balancing 4 |
1 |
741 |
38:27 |
|
Routes 1 + 3 |
2 |
982 |
38:07 |
|
|
3 |
277 |
38:31 |
|
|
Max. imp. route = 3, Min. imp. route = 2 |
||
|
Network balancing 5 |
1 |
741 |
38:30 |
|
Routes 2 + 3 |
2 |
990 |
38:14 |
|
|
3 |
269 |
38:15 |
|
|
Max. imp. route = 1, Min. imp. route = 2 |
||
|
Network balancing 6 |
1 |
736 |
38:19 |
|
Routes 1 + 2 |
2 |
995 |
38:21 |
|
|
3 |
269 |
38:20 |
Table 132: Example equilibrium procedure (BPR function a=1, b=2)
Table 132 shows how the equilibrium procedure works for the example network (Example network for PrT assignment procedures). The volume determined with the incremental procedure is used here as the initial solution (Example of incremental assignment). This starting solution encompasses two routes, each loaded with 1,000 car trips. The specified absolute deviation is a value of five impedance units, and the relative deviation is specified as being 0.1 %. Based on the starting solution, the following steps are then carried out.
- Network balancing for starting solution
The volumes of the routes 1 and 2 are changed in such way that the deviation of the two route impedances is below the specified deviation. With a volume of 776 respectively 1,224 vehicles for routes 1 and route 2, this is guaranteed.
- Route search for iteration step 1
After network balancing of routes 1 and 2, the shortest path search of the first iteration step determines route 3.
- Network balancing for iteration step 1
The three routes are balanced in pairs until the impedance of all routes accords with the specified deviation.
This is the case in the example if one of both conditions applies:
- The absolute deviation between maximum and minimum impedance is smaller than 5 seconds.
- The relative deviation between the maximum and minimum impedance is less than 0.1 %.
- Network balancing by pairs always changes the volumes of the route with the minimum impedance and the route with the maximum impedance.
- Route search for iteration step 2
No new route is found, the equilibrium procedure terminates.