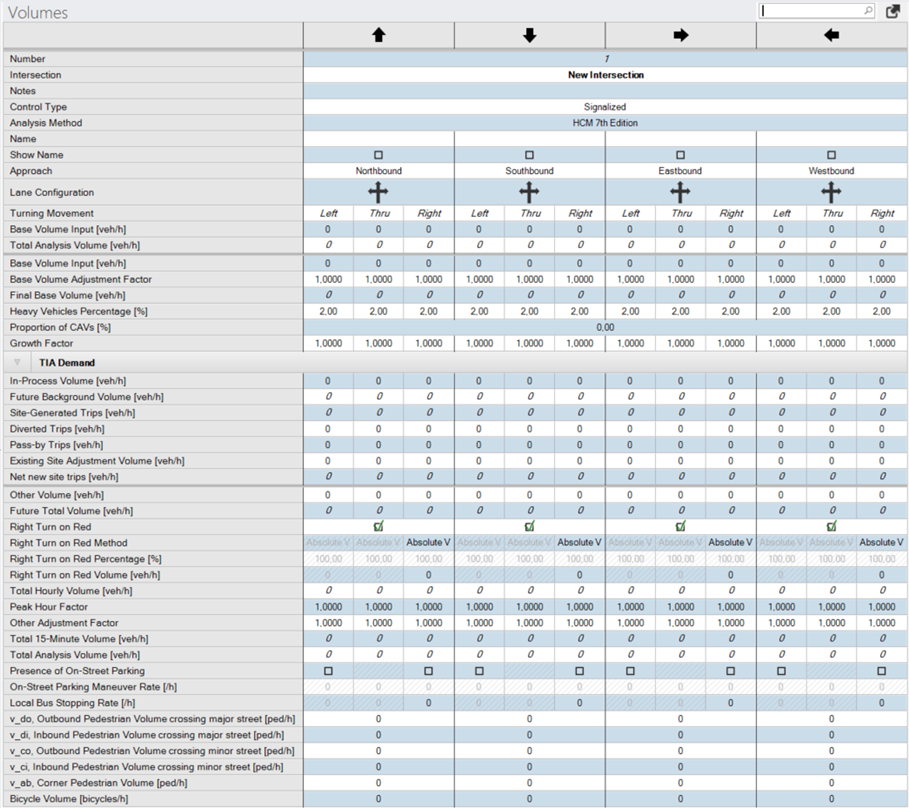
Volumes
One of PTV Vistro’s most powerful features is its trip accounting capability. With PTV Vistro there are multiple layers of volumes and adjustments that can be entered to result in the desired analysis volume. When performing a traffic impact analysis (TIA) in PTV Vistro, trips associated with a development are automatically calculated for each turn movement in the network once the trip generation, distribution, and assignment have been performed. Additionally, PTV Vistro provides place holders to make volume adjustments, such as in-process trips from an already approved, but not yet built development that needs to be included in the analysis.
In the case of a non-TIA project, all of the TIA-related parameters are grouped together and can be collapsed in the volume setup table by using the arrow button to the left of the TIA Demand header. Parameters that appear italicized in the volume setup table are calculated values. The Volumes workflow task table is shown below in the figure of the Volumes Table.
All parameters in the volume setup table are described in the table Volumes Parameters below the figure.
| Parameter | Description | Units | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Basic Volume Inputs |
||||
|
Number |
Unique number of the intersection. Intersections are numbered consecutively. However the preset number may be overwritten by another number that does not already exist in the network. |
|
||
|
Intersection |
Name of Intersection |
|
||
|
Approach |
Direction of approach as defined under the intersection setup table. |
|
||
|
Lane Configuration |
Shows lane configuration as defined in intersection setup table. |
|
||
|
Turning Movement |
Identifies the movement (Left, Thru, Right, U-Turn) |
|
||
|
Base Volume Input |
Summary of Base Volume Input, description below. |
veh/h |
||
|
Total Analysis Volume |
Summary of Total Analysis Volume, description below |
veh/h |
||
|
Base Volume Input |
Base traffic volume input by user. |
veh/h |
||
|
Base Volume Adjustment factor |
User definable adjustment factor to apply if desired to base volume input. An example application would be a seasonal adjustment factor. Default = 1.0000. Range = 0 - 99.9000 |
|
||
|
Final Base Volume |
Base volume representing the base condition. = Base Volume Input * Base Volume Adjustment Factor |
veh/h |
||
|
Heavy Vehicles Percentage |
Percent of heavy vehicles for each turn movement. Default = 2. Range = 0 – 100 |
|
||
|
Proportion of CAVs [%] |
Proportion of CAVs (connected and automated vehicles) in traffic stream, Range is [0.00;100.00], (HCM 7th edition) |
|||
|
Proportion of EVs [%] |
Proportion of EVs (electric vehicles) in traffic stream, Range is [0.00;100.00], (HCM 7th edition) |
|||
|
Growth Rate |
Growth rate to be applied as multiplicative factor to adjust volume to future year analysis. Default = 1.000; |
|
||
|
TIA Demand |
||||
|
In-Process Volume |
User definable volume input typically used to account for trips already approved by a nearby development that is not yet in place. |
veh/h |
||
|
Future Background Volume |
Future volumes before any trips are added for the new development. = Final Base Volume * Growth Rate + In-Process Volume |
veh/h |
||
|
Site-Generated Trips |
Trips calculated from the new development(s) based on the trip generation, distribution, and assignment paths. Making changes to any component of the trip generation process will result in a change to this value. |
veh/h |
||
|
Diverted Trips |
Trips attracted from the traffic on roadways within the vicinity of the development site but require a diversion from that roadway to another roadway to gain access to the site. Diverted trips add traffic to the roadways adjacent to a site. Value may be negative or positive. |
veh/h |
||
|
Pass-by Trips |
Trips made as intermediate stops to the development on the way from an origin to a primary trip destination. This field is used in tandem with the Trip Generation for a zone. Primary trips (non-pass-by) can be generated and assigned to the study network, while pass-by adjustments at project driveways can be entered in these fields. Value may be negative or positive. |
veh/h |
||
|
Existing Site Adjustment Volume |
User defined volume adjustment to account for trips either added or removed due to changes in the land use to accommodate the new development. For example, an existing apartment complex is removed to allow construction of a new retail shop. In this case, trips from the apartment complex have been accounted for in the base volume and now need to be removed. This parameter may be positive or negative. |
veh/h |
||
|
Net New Trips |
Total new trips added to the system after accounting for all adjustments. = Site Generated + Diverted + Pass-by + Existing Site Adjustment Volume |
veh/h |
||
|
Additional Volume Adjustments and Calculations |
||||
|
Other Volume |
User definable volume not accounted for by other volume parameters |
veh/h |
||
|
Future Total Volume |
Total future volume after all site generated trips and volume adjustments have been made. = Future Background Volume + Net New Trips + other volume |
veh/h |
||
|
Right-Turn on Red Volume |
Volume adjustment to account for vehicles per hour that turn right on a red signal. Value is positive. If the Right Turn on Red Method is set to Absolute, a right-turn on red volume value can be entered If the Right Turn on Red Method is set to Percentage, a right-turn on red percentage value can entered. This value will calculate right turn on red volume based on a percentage of the movement's Future Total Volume. Global Settings or Multi Change can be used to set a default Right Turn on Red Percentage. |
veh/h |
||
|
Total Hourly Volume |
Total hourly future volume after accounting for right-turn on red |
veh/h |
||
|
Peak Hour Factor |
PHF based on the Highway Capacity Manual used to adjust the hourly volume to reflect the 15-minute peak flow rate. Default = 1.0000. Range = = 0.25 – 1.0000 |
|
||
|
Other Adjustment Factor |
User defined adjustment factor to account for factors not accounted for by any other parameter. Default = 1.0000. Range = 1 – 99.9000 |
|
||
|
Total 15-Minute Volume |
Estimated total vehicles during the highest 15-minute period of the peak hour. = (Total Hourly Volume * 0.25 / PHF) * Other Adjustment Factor |
vehicles |
||
|
Total Analysis Volume |
Calculated total analysis volume, including all volume adjustments and factors defined. = Total 15-Minute Volume * 4 |
veh/h |
||
|
Presence of On-Street Parking |
Checkbox to indicate on-street parking is present and a factor in the analysis |
|
||
|
On-Street Parking Maneuver Rate |
Number of on-street parking maneuvers per hour that occur on the approach adjacent to the movement indicated |
#/h |
||
|
Local Bus Stopping Rate |
Number of bus stop maneuvers per hour that occur on the approach |
#/h |
||
|
Pedestrian Volume |
Pedestrian volume on crosswalk of selected approach. This volume is utilized in the HCM (2010 and 2000) calculation and to generate pedestrian input for crosswalks when exporting to Vissim.
|
Peds/h |
||
|
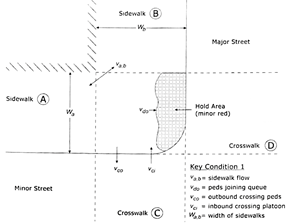
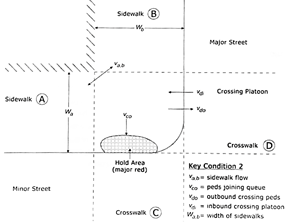
Outbound Pedestrian Volume crossing major street |
Pedestrian volume crossing major street headed away (outbound) from the subject corner (HCM since 6th Edition). The subject corner is the near-side corner on the subject approach on the side of the direction of travel (e.g., right side for right-hand traffic, left side for left-hand traffic).
|
Peds/h |
||
|
Inbound Pedestrian Volume crossing major street |
Pedestrian volume crossing major street headed toward (inbound) the subject corner (HCM since 6th Edition). The subject corner is the near-side corner on the subject approach on the side of the direction of travel (e.g., right side for right-hand traffic, left side for left-hand traffic).
|
Peds/h |
||
|
Outbound Pedestrian Volume crossing minor street |
Pedestrian volume crossing minor street headed away (outbound) from the subject corner (HCM since 6th Edition). The subject corner is the near-side corner on the subject approach on the side of the direction of travel (e.g., right side for right-hand traffic, left side for left-hand traffic).
|
Peds/h |
||
|
Inbound Pedestrian Volume crossing minor street |
Pedestrian volume crossing minor street headed toward (inbound) the subject corner (HCM since 6th Edition). The subject corner is the near-side corner on the subject approach on the side of the direction of travel (e.g., right side for right-hand traffic, left side for left-hand traffic).
|
Peds/h |
||
|
Corner Pedestrian Volume |
Pedestrian volume traveling around the subject corner, not crossing the street (HCM since 6th Edition). The subject corner is the near-side corner on the subject approach on the side of the direction of travel (e.g., right side for right-hand traffic, left side for left-hand traffic).
|
Peds/h |
||
|
Bicycle Volume |
Bicycle volume on the selected approach |
Bicycles/h |
||
Highway Capacity Manual, 6th Edition’s Pedestrian Inputs (Exhibit 19-29 and 19-30)