
Tip: Network files, including examples, can be found in the folder ..\Documents\PTV Vision\PTV Viswalk 11\Queuing:
- 04 Service Points.inpx
- 04 Service Points 2.inpx
You can use the Service point selection method to perform dynamic pedestrian routing.

|
Tip: Network files, including examples, can be found in the folder ..\Documents\PTV Vision\PTV Viswalk 11\Queuing:
|
The route choice method Service point selection is suited for the following use cases:
To model a single joint queue for multiple service points. In reality, the "first come – first served" principle is practiced in post offices, at train stations or airports. Pedestrians are not only queuing in front of the service points, but they may also wait in areas in front of these points. The Queue attribute of the area which relates to the partial route decision must be selected. The area is thus turned into a queue area.
A simple decision model for multiple service points. The pedestrians wait at each service point with a separate queue. The pedestrian has to decide which queue to join. Normally, pedestrians will choose the queue with the shortest waiting time. However, it is not easy to tell which one that is, particularly when there is a large number of service points and/or queues, e.g. at supermarket checkouts or ticket gates. The Queue attribute of the area in front of the service points must be selected. The areas are thus turned into queue areas.
Individual pedestrians walking by are asked to stop for a minute, e.g. to answer a few questions in a questionnaire. Afterwards, they continue their route.
Pedestrians affected by this partial routing decision can be influenced in their routing behavior as follows:
The service point is the first queue area on the course of the route that includes an intermediate point of the partial route.
|
|
Tip: Your Vissim installation provides modeling examples for test applications: ..\Examples Training\Pedestrians\Queuing\08 - Service Desk Partial Routes - Use Cases.inpx |
In all figures below, the pedestrian streams go from left to right.
| Symbol | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Pedestrian area |
The Queue option is selected. |

|
Pedestrian area |
The Queue option is not selected. |

|
Static routing decision | Route point where a pedestrian route starts (static). In the pictures below, in the left areas in which pedestrian inputs are defined as well. |
|
|
Partial routing decision |
Partial routing decision using the route choice method Service point selection. In the pictures below, in the waiting areas. |
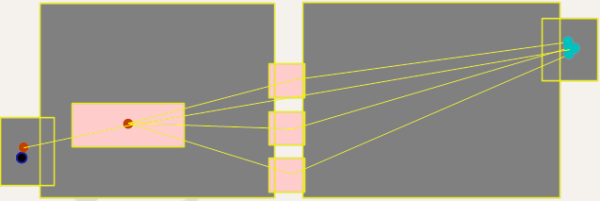
Typically, the queue threshold nis as follows: Proceed to service point if no more than __ people are queuing there = 0.
This ensures that there is no queue at the service point.
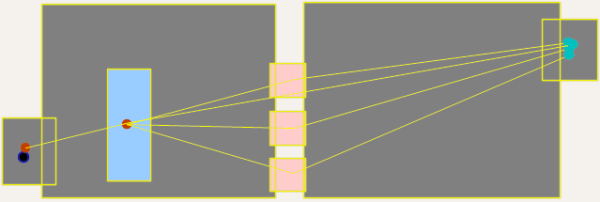
Typically, the queue threshold nis as follows: Proceed to service point if no more than __ people are queuing there = 99.
This ensures that all pedestrians join a queue.
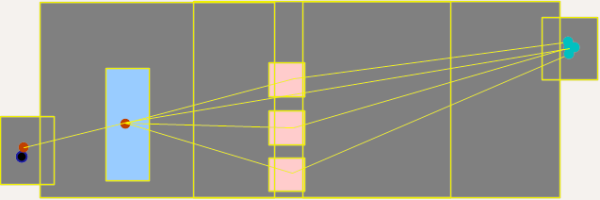
Typically, the queue threshold nis as follows: Proceed to service point if no more than __ people are queuing there = 0.
This ensures that there is no queue at the service point.
Superordinate topic:
Information on editing:
Defining the Dynamic Potential for a static pedestrian route
