 .
.You can create a user-defined attribute in the Base data menu or the Attribute selection window (Selecting attributes and subattributes for columns of a list).
1. From the Base Data menu, choose > User-defined attributes.
The User-defined attributes list opens. If no user-defined attribute is defined, only the column titles are displayed.
2. In the list, on the toolbar, click the Add button  .
.
The User-defined attribute window opens.

|
Tip: Alternatively, you can also open the User-Defined Attribute window via the following functions: When doing so, you adopt the network object type as the object type of the user-defined attribute.
|
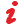
|
Note: In lists, you can use the |
3. Make the desired changes:
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Object type |
Object type of user-defined attribute (mandatory field) In addition to the network object types, you can select other object types, such as Network settings (NETPARA). For NETPARA, choose the data source type Formula to enter a formula value that you can use as a user-defined constant. Select TableLookup to access NETPARA. |
| Short name |
Abbreviated name of user-define attribute (mandatory field) |
| LongName |
Full name |
| Comment |
Optional comment |
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Data type |
A user-defined attribute must have a data type. Select the desired entry. |
|
Data types allowed: |
|
| Acceleration |
Acceleration |
|
Bool |
Enables logical statements for a user-defined attribute that can be assigned 0, 1, or no value:
|
|
Filename |
Filename: Reference to a file, for example for a user-defined attribute, which lists where to find further information. |
|
Duration (integer) |
Time [s] without decimal separator |
|
Duration (floating-point number) |
Time [s] with decimal separator |
|
Area (km2) |
Square kilometers |
|
Area (m2) |
Square meters |
|
Integer |
Integer without decimal separators |
|
Speed (km/h) |
Speed (km/h) |
|
Speed (m/s) |
Speed (m/s) |
|
Floating-point number |
Floating-point number with decimal separators |
|
Length (km) |
Length (km) |
|
Length (m) |
Length (m) |
|
Length (mm) |
Length (mm) |
|
Text |
String |
|
Currency |
Currency |
|
Time |
Time in format hh:mm:ss (12:23:12) or hh:mm (12:23) |
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
|
Subattributes |
The values of the user-defined attribute are recorded for each simulation run. When you show the user-defined attribute in an attributes list, the attribute values are listed per column for each simulation run.
|
4. Select the desired data source type.
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
Allow empty value |  If the option is selected, no value may be specified for the user-defined attribute. By default, the option is not selected and the default value is NULL. If the option is selected, no value may be specified for the user-defined attribute. By default, the option is not selected and the default value is NULL. |
Default value | Optional entry of a default value |
Minimum |
|
Maximum |
|
Decimal places | Number of decimal places for a value with decimal separator |
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
Decimals | Number of decimal places for a value with decimal separator |
If the attributes selected for the formula are based on dynamic data that can change during a simulation run, the values of the user-defined attribute displayed in a results or attribute list can also change during the simulation run.
Syntax errors are highlighted in red:
Vissim highlights formula syntax errors in red. Below the entry box for the formula, a message is displayed with information on the possible cause of the syntax error.
5. Confirm with OK.
The User-defined attribute window closes. The user-defined attribute is displayed in the User-defined attributes list.
The user-defined attribute ConflGap will calculate the gap in front for the two links of a conflict area, if Link1 has the Status2 and Link2 has Status1.
For this example the following data are selected or entered:
In the Insert TableLookup window:
In the Formula entry box, change entry TableLookup(CONFLICTAREA ca; ; ) to:
TableLookup(CONFLICTAREA ca; ca[LINK1\NO]=[NO] & ca[STATUS]=2 | ca[LINK2\NO]=[NO] & ca[STATUS]=1;ca[FRONTGAPDEF])
The user-defined attribute ConflGap is then available as an attribute of the network object type Link. In the Links list, you can show ConflGap as a column. You can also show the Front gap value for each link in the list that has conflict areas with the two statuses defined.
Superordinate topic:
